Note:
Analysis tools are now available in Map Viewer, the modern map-making tool in ArcGIS Enterprise. To learn more, see Perform analysis (Map Viewer).
Below you'll find information about accessing and using the analysis tools.
Licensing
The administrator of your organization must grant you certain privileges for you to perform analysis. To use any of the analysis tools, you need the following privileges:
- Create, update, and delete content
- Publish hosted feature layers
- Standard Feature Analysis
These privileges are available with a Creator, Professional, or Professional Plus user type and a Publisher or Administrator role. If you do not have these privileges, you will not see the Perform Analysis option as described below.
Certain tools need additional privileges such as Network Analysis and GeoEnrichment. See Perform analysis for more information about these tools.
Access the tools
To access and use analysis tools in Map Viewer Classic, follow these steps:
- Open a web map containing the feature layer or layers you want to analyze in Map Viewer Classic. For more information, see Supported data for spatial analysis tools.
- Click the Contents button in the Details pane.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Analysis button
 on the map menu bar.
on the map menu bar. - Hover over the layer you want to analyze and click the Analysis button
 .
.
- Click the Analysis button
- If raster analysis is enabled for your account, choose either Feature Analysis or Raster Analysis.
The Perform Analysis pane appears.
Explore the Perform Analysis pane
The Perform Analysis pane is illustrated below. This pane contains a number of categories, and each category contains tools. To view the tools in a category, click the expand or collapse button on the left side of the category.
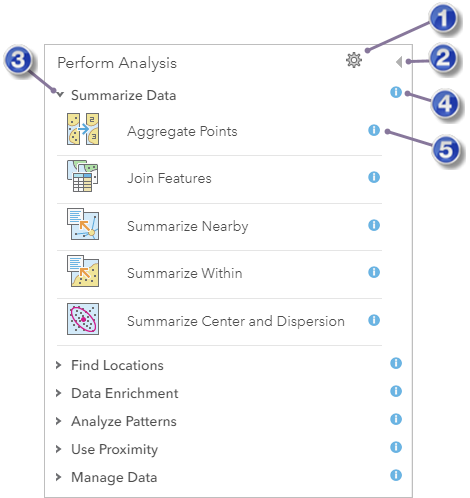
 | Open the Analysis Environments dialog box. |
 | Return to the Details pane. |
 | Expand the category to view the tools it contains. |
 | View help about the category. |
 | View help for the tool. |
Use the analysis environments
The Analysis Environments button  is used to access settings that are applied to all tools run from your map. The Analysis Environments window can be used to change the processing extent (the extent of the data used during the run of the analysis). The processing extent can be set as one of the following three options:
is used to access settings that are applied to all tools run from your map. The Analysis Environments window can be used to change the processing extent (the extent of the data used during the run of the analysis). The processing extent can be set as one of the following three options:
- Default—The tool uses the extent of the data specified by the tool being run. If a tool has Use current map extent checked, only features in the visible extent are used. If Use current map extent is not checked, all features are used. This option is the default. When this option is selected, Use current map extent is checked by default.
- Layer < layer name >—The tool uses the extent of a layer included in the map for processing. When this option is selected, Use current map extent is not checked by default. Checking Use current map extent overrides using the selected layer's extent.
- As specified—The tool uses an extent you provided by typing the coordinates using the Web Mercator projection. When this option is selected, Use current map extent is not checked by default. Checking Use current map extent overrides using the selected layer's extent.
Work with a tool pane
To open an analysis tool pane, click the tool button. This opens the tool's pane as illustrated below with the Aggregate Points tool.
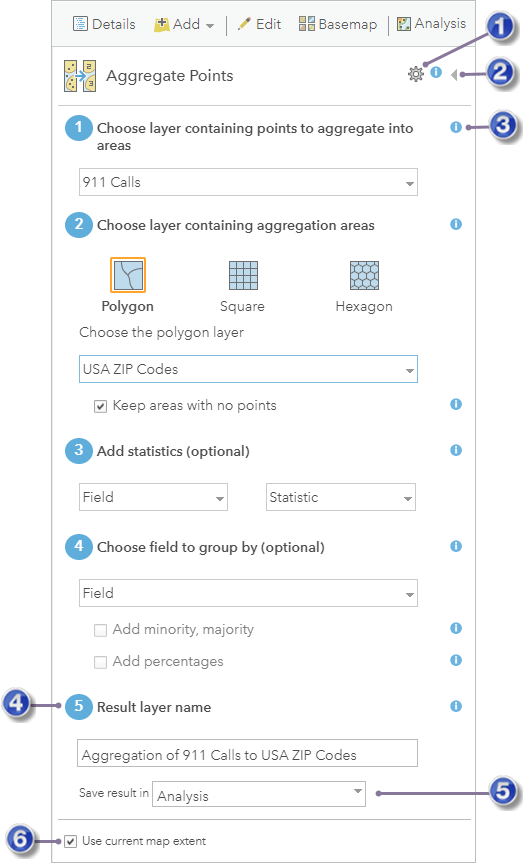
 | Open the Analysis Environments dialog box for the tool. |
 | Close the tool pane without running the analysis and return to the Perform Analysis pane. |
 | Get help about a parameter. |
 | The result of running the analysis is saved to Content using this name. |
 | You can specify a folder in Content in which to save the result. |
 | If checked, only the data visible in the current map will be analyzed. |
Note:
Analysis environments can be set from the tool pane. Processing Extent is the only environment that is used by the spatial analysis tools. The Processing Extent setting applies to all tools, even when the extent is set in a tool pane. The Use current map extent parameter will be unchecked when Processing Extent is set. Checking Use current map extent will override Processing Extent.
Each tool has a different set of parameters. You can view help for a parameter by clicking the help button next to the parameter as illustrated above. All tools have a Result layer name parameter where the results of running the analysis are written. You can change this name or use the default value.
Use current map extent
It is recommended that you always check Use current map extent and that you zoom in to the area you want analyzed. Doing so limits the number of features the tool needs to examine when performing analysis. It also limits the number of credits that may be used by the tool if it is configured to use utility services from ArcGIS Online. If you uncheck Use current map extent, all features in the analysis layer will potentially be analyzed, and ArcGIS Online credits used by the tool will be based on the number of features in the layer.
Rerun analysis tools
Analysis tools can be rerun by clicking the Rerun Analysis button  for a result feature layer. Rerun Analysis will open the tool that was used to create the layer and repopulate all of the parameters. The tool can be rerun with the same parameters, or the parameters, including inputs, can be updated before the tool is run.
for a result feature layer. Rerun Analysis will open the tool that was used to create the layer and repopulate all of the parameters. The tool can be rerun with the same parameters, or the parameters, including inputs, can be updated before the tool is run.
Note:
Rerun Analysis is not available for results created as feature collections.
When rerunning analysis tools, the state of the current map will be honored, including filters, extent, input layers, and output folder. To ensure that an analysis is rerun at a specific extent, create a bookmark. If you share your results with the intention of allowing other users to rerun your analysis, you may need to share your input layers as well. If you open a tool using Rerun Analysis and the input layers are not available, a warning appears but the tool can still be run with different inputs.
Note:
The Result layer name from the previous iteration will be used when you open an analysis tool using Rerun Analysis. You must create a unique name before rerunning a tool.
Analysis output
Most analysis tools that are run in Map Viewer Classic create hosted feature layers as output. These output layers are projected in the spatial reference of the input layer.